Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

The evolution of 3D art and animation has dramatically transformed digital media. It began with simple wireframe models and evolved into highly detailed, lifelike visuals used in film, gaming, and virtual reality. Early software like Blender, 3ds Max, and Maya allowed artists to create complex models and bring them to life with realistic textures and animations. Today, 3D art extends beyond entertainment, influencing industries like architecture, medical visualization, and product design, making it a vital part of modern digital artistry.

The journey of 3D art started with basic wireframe models and low-polygon graphics. Artists could build simple structures, but the technology at the time limited the level of detail. Software such as CAD programs played a significant role in this period, allowing engineers and artists to experiment with three-dimensional shapes in virtual space.

The 1990s and early 2000s saw rapid advancements in 3D software capabilities. Tools like 3ds Max, Maya, and Blender introduced features for detailed modeling, realistic textures, and complex lighting effects. The emergence of 3D animation in films, such as Toy Story (1995), showcased the potential of computer-generated imagery (CGI), setting the stage for mainstream adoption.

The gaming and film industries embraced 3D art to enhance visual storytelling. Games like Final Fantasy and movies such as Avatar (2009) demonstrated how 3D graphics could create immersive worlds. The use of motion capture technology allowed for more realistic character animations, blending human performances with digital artistry.
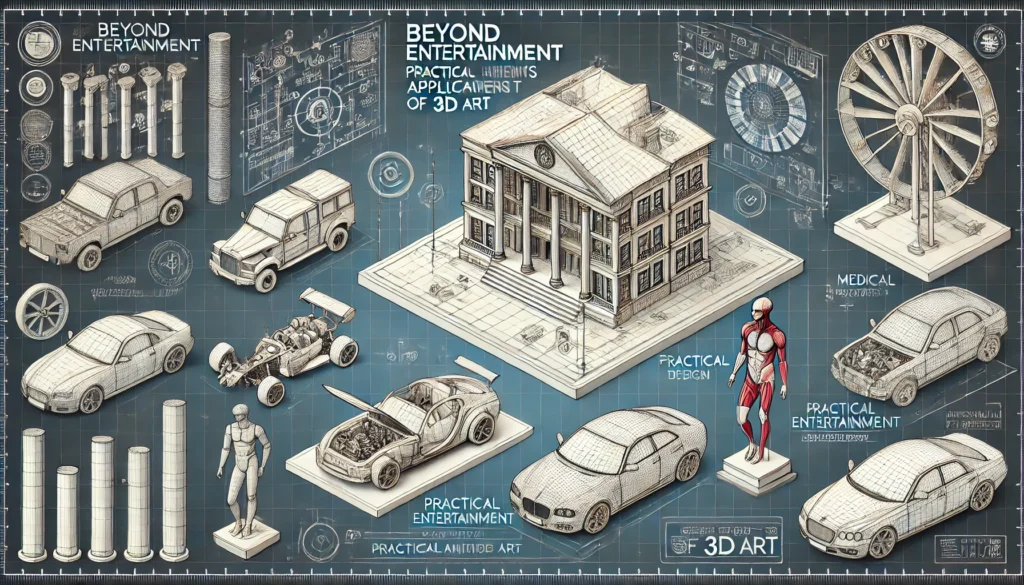
Today, 3D art extends well beyond entertainment, finding applications in architecture, medical visualization, automotive design, and virtual reality experiences. Architects use 3D models to visualize building projects, while surgeons employ 3D-printed models for planning complex procedures.

The future of 3D art is driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and real-time rendering technologies. Tools like Unreal Engine enable artists to create photorealistic visuals in real-time, while AI-powered software can automate complex tasks like texture mapping and animation.
Conclusion: From Wireframes to Realism
The journey of 3D art has been one of continuous innovation, from simple wireframes to highly detailed digital sculptures. As technology continues to evolve, the possibilities for 3D artists are limitless, reshaping how we interact with digital media and the world around us.